Keeping your network safe is invaluable to its performance, reliability, and longevity. Unfortunately, it’s easy for attacks to occur in your IT environment—bad actors today are smarter than ever and can often break into your systems undetected. Security logs, which are put in place to record and discover security problems, can be modified by malicious software or simply amended by accident. For this reason, it’s crucial to perform sufficient security log management.
The more network devices present in your network, the more potential there is for security issues to stem from insufficient log monitoring. There are many best practices you can put in place to enforce security log integrity, but the most effective and simple way is to use a security log analyzer. Security log analyzers present you with vital information about your network’s security and ensure accuracy in your security logs.
You may find a security log tool useful if:
- The infrastructure of your company allows access to databases, servers, or systems to many users, whose activity must be controlled
- Checking security logs is a critical task on which the safety of your organization’s data and computer systems depends
- The existing log analysis tools in your computer environment are difficult to use and clumsy, and you want accurate and timely log analysis
- You must be kept informed of suspicious events or anomalies in security logs
My recommended choice is SolarWinds® Log Analyzer, which is designed to investigate security log data and identify key events, root sources, and suspicious activity that could indicate security breaches. A 30-day free trial of Log Analyzer is available for download and an interactive demo you can use.
What’s the Difference Between Security Logs and System Logs?
Best Practices for Security Log Management
Recommended Tool for Security Log Management
Get Started With Security Logging and Management
What’s the Difference Between Security Logs and System Logs?
Simply put, system logging creates a record of all activity, transactions, and changes in your IT infrastructure. System logs include data like user IDs, files and networks accessed, usage of system utilities, and log-ons and log-offs. Your servers and devices accumulate tens of thousands of log entries each day, with each log entry representing a single event. The perception that system logs contain mostly routine data is dangerous—you must capture, store, and analyze log data consistently to address performance issues, understand network capabilities and requirements, and prepare for the future.
Security logs track events specifically related to the security and safety of your IT environment. This could include alarms triggered, activation of protection systems and intrusion detection systems, and successful and failed attempts to access systems, applications, or valuable data. Security logs contain a wealth of information to help you reduce exposure to intruders, malware, and data loss in your network. You could also reference security logs to notice various exceptions and outlier situations.
Microsoft-based systems generate Windows Server security logs, which provide key information on who’s logged in to your network and what they’re doing. Windows Server security logs also help those dedicated to network safety understand the vulnerabilities present in already-existing security implementations. If you’re unfamiliar with Windows Server security logs, you may have a few questions:
Where are Windows security logs stored? Windows security logs can be found in the Windows or WINNT directory, under the Event Viewer. Windows Server security logs are controlled by the Local Policy/Audit Policy settings.
How do I read Windows Server security logs? After you’ve accessed the Windows Server security log through the Event Viewer, you can scan through security-related events. Monitor changes and attempted changes to folder or file permissions, known as file auditing, in two different views: global view, which shows all events, or by viewing each file or directory individually.
How to read security logs differs for every operating system, as each system has its unique way of displaying security logs. But no matter which OS you use to create your security log, you must access and read those security logs regularly to help detect vulnerabilities in your network, including those from within, so you can better protect your data.
Best Practices for Security Log Management

Here are some security logging best practices you should follow to help protect your network from unauthorized users, malware, and data loss or modification.
1. Define Your Goals
It’s important you and your team members are clear in your business’s security goals. This will help counter unwanted amendments from within your organization and ensure everyone is on the same page when it comes to data protection. You should also verify your security log goals align with all applicable laws and regulations.
In the Microsoft Windows lexicon, this is known as “Audit Policy Categories.” Audit Policy Categories signify the kinds of security events you want your network security logs to record. You can set these by hand or through the uniform Audit Policy settings, depending on which Windows system your organization uses.
2. Ensure Internal and External Integrity
You must be able to trust the integrity, or incorruptibility, of your network security logs. Unwarranted amendments could come from outside your organization or within, so you should define security log goals with team members and create internal policies focused on data retention and accuracy. Internal threats, such as an employee who wants to change permissions to access confidential information, can be prevented by using replicas or read-only files in your security logs.
While some external threats could be mitigated with firewalls, it’s not enough to rely on their ability to protect your network data. Bad actors will often try to alter security log files in attempts to hide their presence, preventing in-place security measures from doing their job. Compromised logs could hinder investigations into suspicious security log events and invalidate evidence for legal action.
One security logging best practice that could counter tampered security logs is to record logs locally and to a remote log analyzer. This practice provides redundancy, adding an extra security layer—compare the two security logs side by side to notice any differences indicative of suspicious activity.
3. Synchronize and Consolidate Events
To best read security logs and analyze their findings, try to keep all your security log data in one place and in the same time zone. Synchronize your system clocks to record time in a consistent format such as Universal Coordinated Time (UTC) and check your system clocks often to correct significant time variations. This will help you understand security events in an accurate context with one another, and with limited movement and confusion.
Maintaining consistent timestamps throughout your security logs is especially important when monitoring multiple OSs in real time. For example, you may want to use Windows server security logs in coordination with Linux systems. If so, you’ll have to make sure each system is on the same time, so you can accurately compare security log events.
When using multiple security log systems, or even when using Windows—whose event logs are decentralized by default, meaning each network device logs its own event activity—it’s best to keep all security log data in a single place for easy access and analysis. Consider the number of devices, users, and IT administrators accessing and contributing to security logs, which will affect how many security logs need to be consolidated.
4. Use a Security Log Analyzer
Log analyzers reveal potential vulnerabilities by automatically file auditing and analyzing network security logs. You can use the information generated by a log analyzer to improve security implementations in place, discover areas for improvement, and gain in-depth knowledge into your network’s security capacities. Log analyzers can also provide a basis for security awareness training, security log policy enforcement, and recognizing network misuse.
Log analyzers are designed to generate reports of security log events, allowing for customization while ensuring accuracy of their data. Some log analyzers can create alerts and notifications that correspond to certain thresholds, enabling you to focus on what’s important while remaining on top of security log management. Your log analyzer can put controls in place to ensure ample security log storage is available, so resources are allocated fairly. Using a log analyzer ensures archived security logs and current security logs maintain their integrity, so you can trust the information coming from your log analyzer.
These security logging best practices can help you make the most of your security log information. Investing in a security log analyzer will help streamline these best practices and more, so you can make informed decisions about your network security and improve security log management.
Recommended Tool for Security Log Management
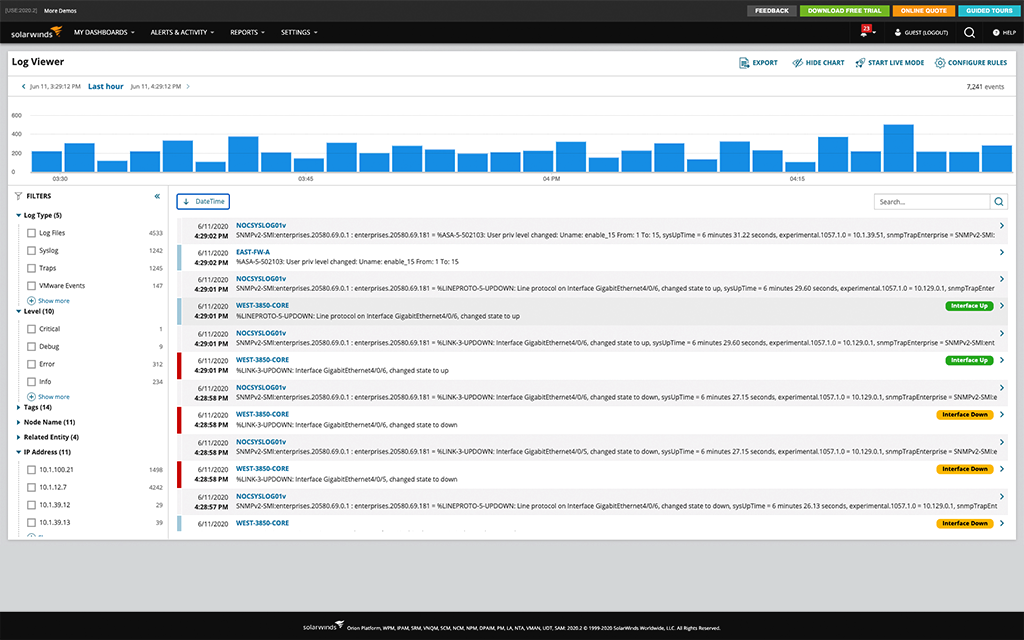
My top recommendation for a security log management tool is SolarWinds Log Analyzer. Log Analyzer is designed to provide insights into your IT environment’s performance by aggregating log data and filtering through security events. Log Analyzer can identify security logs by severity level, vendor, IP address, and more through intuitive filters. This enables you to get crucial security log data without breaking a sweat, breaking the bank, or draining excessive resources.
© 2021 SolarWinds Worldwide, LLC. All rights reserved.
Log Analyzer is built to continuously monitor security log data, identifying potential issues as they occur and quickly exposing their root causes. Security logs are charted in real time, and Log Analyzer enables you to maintain consistent and accurate timestamps. Log Analyzer is designed to support live views and archive security logs automatically, enabling you to access previous error messages, exact timestamps of events, and the volume associated with security events.
Log Analyzer supports a powerful keyword search engine designed to understand event IDs and error codes. This allows you to quickly pinpoint logs without using complex query language. You can preserve these filters for later searches, saving you even more time and effort. Access visualizations of log search results, security log volume, and timeframes with interactive charts and real-time log stream.
Get Started With Security Logging and Management
In my opinion, if you’re looking for a tool to help you uphold security log management best practices, Log Analyzer enables you to take control of your security logs without dedicating too many resources to this one task. Log Analyzer is fully compatible with Windows Server security logs and other security log servers, and is built to allow you to consolidate all your event log information in one place for a clear and comprehensive understanding of overall network performance. Create powerful alert actions, enable email and mobile push notifications, and run external scripts using the Orion® Platform integration with Log Analyzer. In addition to the daily work of analyzing the security logs of various systems, quick detection and alerting of anomalies allows us to maintain the security of systems at the highest level, so I personally recommend this tool to test. Download a 30-day free trial of Log Analyzer or access their interactive demo today to begin expertly tackling security log management and optimizing network security.
