Both MySQL and Microsoft SQL Server (MSSQL) are widely used enterprise database systems. MySQL is an open-source relational database management system (RDBMS), while MSSQL is a Microsoft-developed RDBMS. Enterprises can choose between multiple MSSQL editions to suit their individual needs and budgets. Savvy programmers and database administrators (DBAs) should think carefully about the difference between MSSQL and MySQL before making their decision to ensure they choose the right RDBMS for their requirements.
This guide will consider the difference between MySQL and MSSQL, in addition to making a detailed MySQL vs. MSSQL performance comparison. If you’re looking for reliable database performance monitoring and analysis tools, you should consider SolarWinds® Database Performance Analyzer and SQL Sentry as industry-leading solutions.
Database Monitoring and Analysis Tools
Getting Started With Database Monitoring
MySQL vs. SQL Server
SQL is the ideal language of choice for relational databases, whether you want to retrieve, edit, or store your data—which is how dynamic applications and websites perform practically every user request. Before engaging in a more nuanced MySQL vs. MSSQL performance comparison, let’s first look at some of the basic similarities and differences between MSSQL and MySQL.
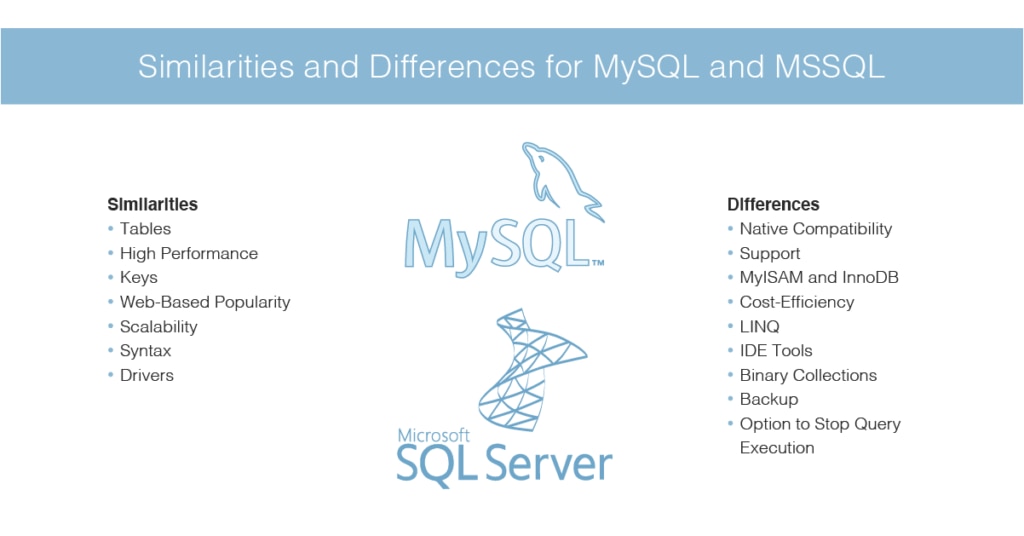
Similarities Between MySQL and SQL Server
As both MSSQL and MySQL are relational databases, there are several similarities. Most developers, however, specialize in either one or the other. Although MSSQL and MySQL seem similar, their underlying architecture differs. Here are the key similarities you should know.
Primary and Foreign Keys
Both platforms use primary and foreign keys to establish the relationships between tables.
Database Performance Speed
Your database is the backbone of your applications and is responsible for storing and returning data as quickly as possible. Both MySQL and MSSQL offer high-performance speed.
Relational Database Table Model
Both platforms use the standard relational database table model for storing data in columns and rows.

Usage Popularity
Aside from Oracle, MySQL and MSSQL are the most common databases for use with web applications. When you sign up for hosting, you’re usually given the choice between MSSQL and MySQL.
Scalability With Different Projects
Both platforms can scale with your company as it grows. They’re suitable for small and large projects and can support millions of transactions every day.
Syntax for Platforms
When working with databases like MySQL and MSSQL, developers interact with data using SQL (Structured Query Language) queries. While SQL is a standardized language, you should expect some small differences across varying CRUD (create, read, update, delete) statements.
Differences in Syntax
MySQL Syntax
- Follows the ANSI SQL standard with variations and additional features specific to MySQL.
- Case-insensitive by default for table/column names and string comparisons.
- Supports both single (”) and double (“”) quotes for string literals.
- Provides a rich set of date and time functions.
- Uses the LIMIT clause for restricting the number of rows returned by a query.
- Offers native support for full-text search.
MSSQL Syntax
- Adheres to the ANSI SQL standard with its syntax and features.
- Case-insensitive by default for table/column names and string comparisons.
- Primarily uses single quotes (”) for string literals.
- Provides comprehensive date and time functions.
- Utilizes the TOP clause to limit the number of rows a query returns.
- Offers full-text search capabilities through specific predicates.
Connection Drivers
Fortunately, you can find connection drivers for almost any popular language just by searching the web. This allows you to easily connect to both MySQL and MSSQL without the need for complicated coding.
MSSQL was introduced in 1989, while MySQL was introduced in 1995 as an open-source project. This makes MSSQL several years older than MySQL. As both solutions have been in production for over two decades, they both have a strong foothold in the market. MySQL can run on either Linux or Windows, as part of a LAMP environment. MSSQL runs on Windows and is usually part of a Windows environment.
Both MySQL and MSSQL can handle small and large software projects, so users should anticipate similar performance levels. No matter which of these servers you choose, performance will primarily rely on your DBA’s ability to optimize queries and code.
Differences Between MSSQL and MySQL Server
Although these platforms are similar, especially in the interface and basic relational database standards, they operate very differently. Most of these differences are accounted for by the underlying architecture and happen in the background, which means they often go unnoticed by the average user. It’s important, however, for DBAs to understand these differences because they play a significant role in your decision-making process.
Multiple Programming Languages Support
Both MySQL and MSSQL support multiple programming languages, including Java, C++, PHP, Ruby, Python, Delphi, Visual Basic, Go, and R. MySQL supports additional languages like Tcl, Scheme, Perl, Eiffel, and Haskel. Because MySQL is so versatile in its support for programming languages, it’s popular among many developer communities. While you can use both database types for Windows and Linux projects, MySQL works natively with PHP, and MSSQL is mainly used with .NET. Integration is simpler using MySQL for PHP and MSSQL for Windows projects.
Option to Stop Query Execution
In MySQL, users can stop a specific query thread using the `KILL` command. However, there isn’t a built-in mechanism to halt a query without terminating the entire connection.
In MSSQL, users can truncate a database query while it’s running without stopping the complete process. This provides more precise control over query execution, ensuring data integrity.
LINQ Queries
MSSQL allows you to set up your entity framework classes in .NET, meaning you can get started with LINQ queries. With MySQL, you’d need to download third-party tools if you wanted to use .NET.
How to Back Up data
If you’re using MySQL, you’ll need to back up data by extracting it as SQL statements. The RDBMS provides a tool to block the database while data is backed up. This feature minimizes the chance of data corruption occurring while switching between MySQL versions or editions. The downside is this makes data restoration a time-consuming process because it requires executing multiple SQL statements. MSSQL doesn’t block the database while backing up data, enabling users to back up and restore mass amounts of data with minimal effort.
MyISAM and InnoDB Engines
MyISAM and InnoDB Engines are configurations for MySQL, allowing the developer to perform various design and programming activities. MSSQL doesn’t allow you to specify different engines when you create a database.
Integrated Development Environment (IDE) Tools Used
Both MySQL and MSSQL have IDE tools, but you’ll need to match the right tool with the appropriate server. MySQL has MySQL Workbench and MSSQL uses Management Studio. These tools allow you to connect with the server and manage configurations for architecture, security, and table design.
Binary Collections for Developers
MSSQL and MySQL are designed as binary collections. MySQL allows developers to use binaries to manipulate database files even while running. Database files can also be accessed and manipulated by alternative processes at runtime. Conversely, MSSQL doesn’t allow any process to manipulate or access binaries or database files. If you wanted to achieve this, you would need to run an instance. This eliminates the opportunity for hackers to access or directly manipulate data. As such, MSSQL is more secure than MySQL.

Cost
MySQL offers both open-source and commercial editions, providing users with flexibility in choosing the version that best suits their needs. The open-source edition of MySQL is freely available, making it a cost-effective option for many users. However, for organizations requiring additional features, support, and enterprise-level capabilities, commercial editions of MySQL are available, albeit at a cost.
On the other hand, MSSQL is primarily offered through commercial licensing, which entails purchasing licenses for server usage. While MSSQL provides robust features and support options, the associated licensing costs can be higher compared to the open-source version of MySQL.
When comparing the cost of MySQL’s commercial editions with MSSQL licensing fees, organizations should consider factors such as their specific requirements, budget constraints, and long-term scalability needs. Additionally, evaluating the total cost of ownership, including maintenance, support, and training expenses, can help businesses make an informed decision regarding the most cost-effective database solution for their needs.
Operating Systems Compatibility
SQL Server was originally developed exclusively for the Windows operating system by Microsoft. However, in recent years, Microsoft has expanded compatibility to include Linux platforms, providing enterprises with the option to deploy SQL Server on both Windows and Linux environments. Despite this expansion, SQL Server does not have native support for installation on macOS.
While macOS users do not have direct support for SQL Server installations, alternative methods such as virtualization or containerization solutions may allow for running SQL Server instances on macOS environments.
JSON Support
MySQL provides robust JSON support through dedicated data types and functions, facilitating efficient storage and retrieval of JSON data in applications. Similarly, MSSQL offers JSON support with its data type and functions, ensuring compatibility with JSON-centric applications.
Scalability
MySQL is well known for its scalability, supporting various replication methods like coordinator-agents and clustering to achieve horizontal scalability. In contrast, MSSQL is designed for both vertical and horizontal scalability, featuring options such as Always On Availability Groups and support for distributed queries and partitioning.
Storage Engines
MySQL distinguishes itself with support for multiple storage engines, with InnoDB being the default and widely used option. InnoDB comes with features such as ACID compliance, transactions, and foreign key constraints. Conversely, MSSQL primarily relies on a single storage engine but compensates with a comprehensive feature set, including table and index partitioning, full-text search, and column store indexes.
Choosing the Right Database Monitoring and Analysis Tools
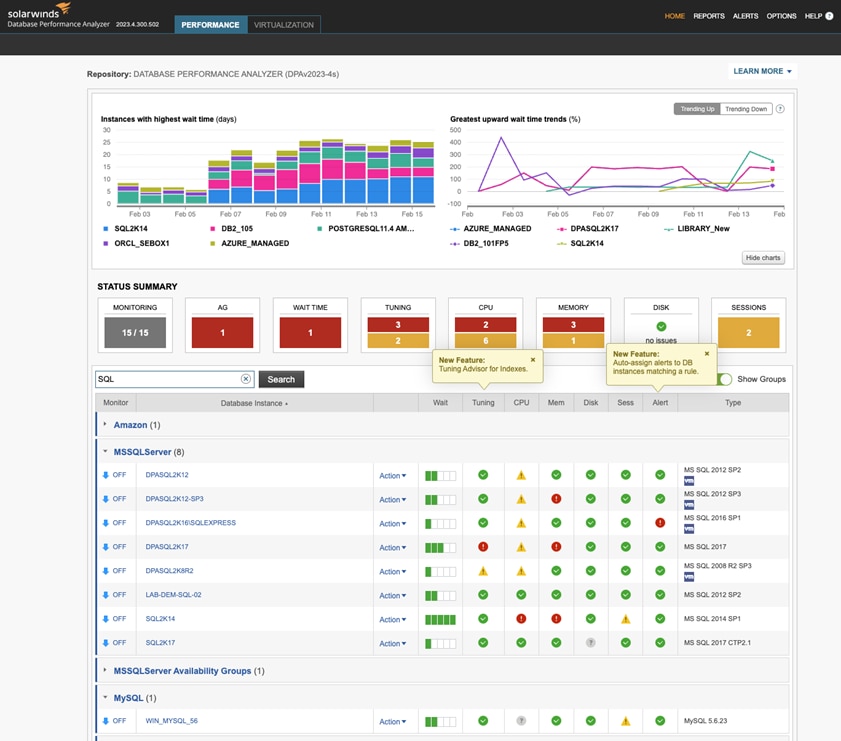
SolarWinds Database Performance Analyzer (DPA)
© 2024 SolarWinds Worldwide, LLC. All rights reserved.
SolarWinds DPA gives you access to response time analytics, helping you correlate activity, wait types, SQL statements, and other dimensions for both MySQL and MSSQL. It provides detailed insight into plans, queries, resources, changes, wait times, and historical analysis, helping you pinpoint the root cause of bottlenecks. DPA’s agentless architecture is safe to use in development, testing, and production and in virtualized and cloud environments. It features an easy-to-use web-based interface that allows teams to collaborate with maximum efficiency. As an MSSQL and MySQL performance monitoring tool, DPA provides multi-dimensional performance analysis through a user-friendly interface. You can start with a 14-day free trial of DPA.
SolarWinds® SQL Sentry
SQL Sentry is designed to help you tackle performance issues in SQL environments more easily. Whether you’re dealing with individual instances or clustered setups, SQL Sentry provides comprehensive monitoring and troubleshooting capabilities. While it can be difficult to troubleshoot the issues after they have occurred, SQL Sentry allows users to review performance over some time, identify when the issue occurred, and troubleshoot it immediately.
© 2024 SolarWinds Worldwide, LLC. All rights reserved.
SQL Sentry can allow you to:
- Monitor SQL Server running in physical, virtual, and cloud environments, such as Azure®
SQL Database, SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS), and Windows® and VMware® hosts. - See historical analysis of performance counters with the ability to go back in time or over a range to see changes in the SQL Server.
- Review top SQL and blocking at specific moments in time, including what queries are running and historical blocking.
SQL Sentry is available in a 14-day free trial.
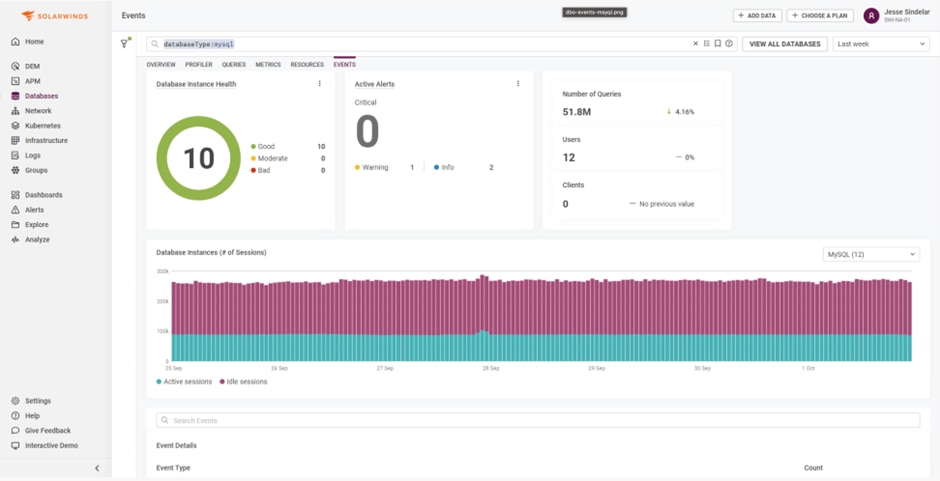
SolarWinds Database Observability
SolarWinds Database Observability stands as a robust solution tailored to address the intricate requirements of modern database performance management. Forming an integral part of the SolarWinds Observability SaaS suite, it empowers organizations to ensure the reliability, performance, and efficiency of their application stack and data tiers.
SolarWinds Database Observability is purpose-built for DevOps environments and seamlessly integrated into the SolarWinds Observability SaaS Solution. It simplifies database performance tuning and monitoring across proprietary and open-source databases. Hosted alongside other SolarWinds Observability SaaS applications, it offers a unified SaaS platform and one-click correlation in context metrics.
This enables proactive monitoring, troubleshooting, and optimization of database ecosystems.
© 2024 SolarWinds Worldwide, LLC. All rights reserved.
Key Features
- Unified Database Monitoring
- Offers a consolidated view of major open-source databases, including MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, Azure SQL, and Amazon Aurora.
- Provides in-depth database performance monitoring at scale, seamlessly integrating with existing database ecosystems.
- Query-Level Monitoring
- Delivers insights into query performance and workload behavior, offering detailed query metrics, execution plans, and historical data for effective query optimization.
- Continuous Health Summaries
- Monitors database and system health in real time, facilitating quick identification of trends, anomalies, and performance outliers.
- Seamless Integration for DevOps Collaboration
- Specifically designed for DevOps environments; seamlessly integrates into workflows to enhance collaboration between development and operations teams.
- Equips both developers and operations engineers with comprehensive database instrumentation and expertise for efficient performance tuning and monitoring.
- End-to-End Observability
- Tracks workloads from applications to the network and into databases, enabling root cause analysis of performance issues across the entire stack.
Key Benefits
- Efficient Performance Optimization
- Optimizes database performance efficiently to ensure smooth application operation and meet user expectations.
- Enables proactive identification and resolution of performance issues.
- Streamlined Troubleshooting
- Correlates query responses with system metrics to rapidly isolate unusual behavior and root causes, simplifying troubleshooting and minimizing downtime.
- Unified View of Diverse Databases
- Provides a unified view of all database types and servers, ensuring stability and scalability across the entire database infrastructure.
- Seamless Cloud Migration
- Simplifies migration from on-premises to the cloud by mitigating challenges associated with cloud migration through comprehensive observability and troubleshooting capabilities.
- Flexible Pricing and Scalability
- Offers pricing based on instances, catering to organizations of all sizes. Can scale to accommodate the needs of organizations with thousands of instances.
Getting Started With Database Monitoring
Both SQL Sentry and SolarWinds DPA are easy to use, navigate, and maintain. The SolarWinds support community is accessible via the THWACK® community, and you get 24/7 access to SolarWinds support technicians if you run into trouble. If you are still unsure which of these tools is right for you, take advantage of the free trials that are available.
How to Set Up a Trial of Database Observability.
Follow these step-by-step instructions to set up a trial of Database Observability:
1. Access the SolarWinds Observability SaaS
2. Click on the “Start Free Trial” button
3. You will then be required to fill out the form on the demo page and Initiate Trial Registration.
4. Submit Registration Form: Once you’ve completed all the necessary fields, review your information for accuracy, accept the terms, and then submit the registration form. Then click on the “Start Free Trial” button. By clicking “Start Free Trial,” you agree to accept the SolarWinds Software Services Agreement and confirm you are authorized to accept these terms on behalf of your company.
5. Access Trial Dashboard: After successful registration, you’ll gain access to the trial dashboard for Database Observability. You’ll receive login credentials or a link to access the dashboard directly.
