Logs can provide vital insights to help you monitor system health, pinpoint and resolve issues, and improve cybersecurity. They capture real-time errors and record information about events and other system activities, shedding light on everything from application performance to security threats.
However, managing logs can be overwhelming. To get the most out of your logs, you need to aggregate them into a centralized system where they can be organized, searched, and analyzed effectively.
Topics covered in this article:
How does log aggregation work?
Why Do Organizations Need Log Aggregation Tools
Common log aggregation methods
- File replication
- Syslog
- Log forwarding
- Application programming interfaces
- Streaming
- Agent-based collection
- Automated pipelines
Steps in the log aggregation process Best Practices for Log Aggregation
- Select a Reliable Protocol
- Secure Log Transfers With Encryption
- Use a Cloud-Based Centralized Log Management Tool
Best Tools for Log Aggregation and Management
What is log aggregation?
Log aggregation involves collecting, standardizing, and consolidating log data from different sources into a single platform. For example, you might gather logs from your organization’s servers, applications, databases, and network devices.
This process enables IT teams to detect patterns, troubleshoot issues faster, and automate responses to critical incidents. Without proper log aggregation, your organization may have fragmented data, making it challenging to maintain visibility, improve performance, and meet compliance standards. With log aggregation, you can capture informational logs that provide details on changes or events within an application, such as new deployments, application loads, or the completion of a scheduled batch job. You can also gather error logs, offering valuable insights into system malfunctions, application crashes, or failed processes. Log aggregation allows the collection of security logs, which can shed light on unauthorized access attempts and other threats.
How does log aggregation work?
Log aggregation works by collecting, centralizing, and organizing log data from different sources across IT environments. You can gather logs from your servers, applications, network devices, and on-premises security systems and collect logs from your cloud platforms and virtual machines (VMs).
Why Do Organizations Need Log Aggregation Tools
There was a time when IT teams maintained logs primarily for compliance and audit purposes. Occasionally, an administrator would inspect the local logs using the tail -f command to troubleshoot a rare issue. However, today logs have become crucial for keeping track of health and performance issues of different applications and IT infrastructure. In modern IT environments, logs are omnipresent. They can originate from an application code instrumented by developers, application servers, message queues like Kafka, load balances, firewalls, routers, and cloud-based services, and more. Inspecting all these logs individually can take time and effort. To meet this challenge, organizations use centralized log aggregators, which help in collecting all these logs in a single location. Many of these cloud-based log aggregators transform and preprocess logs before forwarding them for further processing and indexing.
Benefits of log aggregation
Log aggregation is essential for efficient operations, helping teams quickly address outages and proactively identify patterns to resolve system issues. Once you have correctly aggregated your logs, you will be able to:
- Log collection: The first step in the process is to gather logs from multiple sources. These generally include servers, applications, devices, databases, and cloud services. This can be completed using APIs, agents, and syslog messages.
- Log parsing and normalization: After the logs have been collected, they must be processed and put into a standardized structured format. Parsing involves extracting key information from logs, including timestamps, error codes, and severity levels, simplifying log analysis. Normalizing the logs will allow you to efficiently correlate logs from different data sources.
- Centralized log storage: Aggregated logs should be stored in a centralized location. Usually, this means using on-premises log management or a cloud-based system. This makes logs more easily accessible, which can help when searching logs, demonstrating compliance, or preventing data loss.
- Log indexing: Next, all logs are indexed. This can increase data organization and allow for faster searching and filtering capabilities.
- Log enriching: Some log aggregation tools will add another step and enrich logs with more contextual information. For example, they may add the user ID, geolocation, or log correlation information.
- Log visualization: Log aggregation software also visualizes collected logs in easily understandable formats such as graphs, charts, or heat maps, which you can view using dashboards. With visualization, it’s much easier to spot spikes in errors, performance issues, and unusual activities.
- Alerting: Most log aggregation tools also have an alert functionality, meaning they can instantly notify your team of potential security threats, anomalies, system failures, etc.
- Automation: Some log aggregation solutions even have automated response capabilities. When a predefined condition or anomaly is detected, the tool can automatically act on your behalf. For example, it may restart certain services, block suspicious IP addresses, or send emails to predefined administrators.
Best Practices for Log Aggregation
Select a Reliable Protocol
There are three major protocols for transmitting log data:
- UDP (User Datagram Protocol) – A fast and resource-efficient protocol; however, lacks reliability as it doesn’t require acknowledgment of receipt (ACK). It also doesn’t support secure encryption of logs.
- TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) – Most commonly used protocol for streaming; adds reliability to every message transfer with ACK. However, requirements for the handshake and active connection makes it resource intensive.
- RELP (Reliable Event Logging Protocol) – The most reliable protocol, explicitly designed for Rsyslog. Like TCP it also involves the acknowledgment step and resends the log message if encounters an error. The protocol is commonly employed for log streaming in highly regulated industries unable to afford message loss.
Secure Log Transfers With Encryption
Logs may contain crucial information about customers’ personally identifiable information, financial data, and other business-sensitive data. Threat actors can use sophisticated sniffers to read your log data, and it becomes increasingly exposed when transmitted in clear text over the internet. Ensuring customer data is anonymized is an important step in information security. However, to add another layer of security, all log data should be encrypted using protocols such as TLS.
Use a Centralized Log Management Tool
You can create your own log management setup using open-source tools. However, when using open-source tools, you have to be ready for various configuration challenges. A self-managed logging setup requires multiple complex integrations, constant infrastructure monitoring, and significant time investment in maintenance and upgrades. On the other hand, commercial log management solutions offer quicker provisioning, higher scalability, greater performance, easier integration, dedicated technical support, and all this at a much lower Total Cost of Ownership (Total Cost of Ownership).
Best Tools for Log Aggregation and Management
Log aggregation tools are vital for organizations, as they can simplify the collection, storage, and analysis of log data from several sources. Without centralized logs, detecting security threats, troubleshooting issues, and maintaining compliance with various regulations can quickly become time-consuming and inefficient. On the other hand, the correct log aggregation tool can help you and your team quickly discover anomalies, accurately correlate events across different systems within your IT infrastructure, and automate alerts, enabling you to manage incidents proactively. There are plenty of log aggregation tools on the market, but two popular options are SolarWinds® Kiwi Syslog® Server NG and Papertrail™.
Kiwi Syslog Server NG
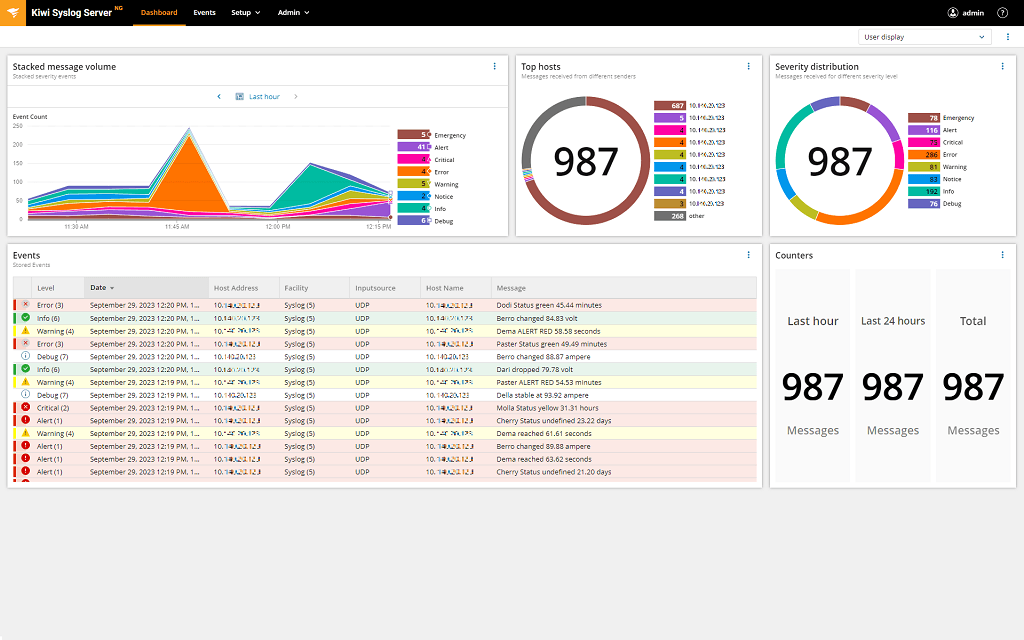
Kiwi Syslog Server NG is a new and improved version of Kiwi Syslog Server. This powerful solution can manage syslog messages, SNMP traps, and Windows event logs, yet it remains affordable and simple to use. Since it can centralize all your syslog messages, Kiwi Syslog Server NG can save you valuable time in discovering the root cause of an issue or resolving network problems.
Kiwi Syslog Server NG has powerful filtering capabilities, meaning you can view messages based on severity, time, hostname, and more. It can also automatically alert you of specific events or even act independently. For example, it can send email notifications; generate reports; run scripts; run external programs; write logs to a file, Windows event log, or database; forward syslog messages and SNMP traps to another host; or split written logs by IP, device, date, or hostname.
Logstash
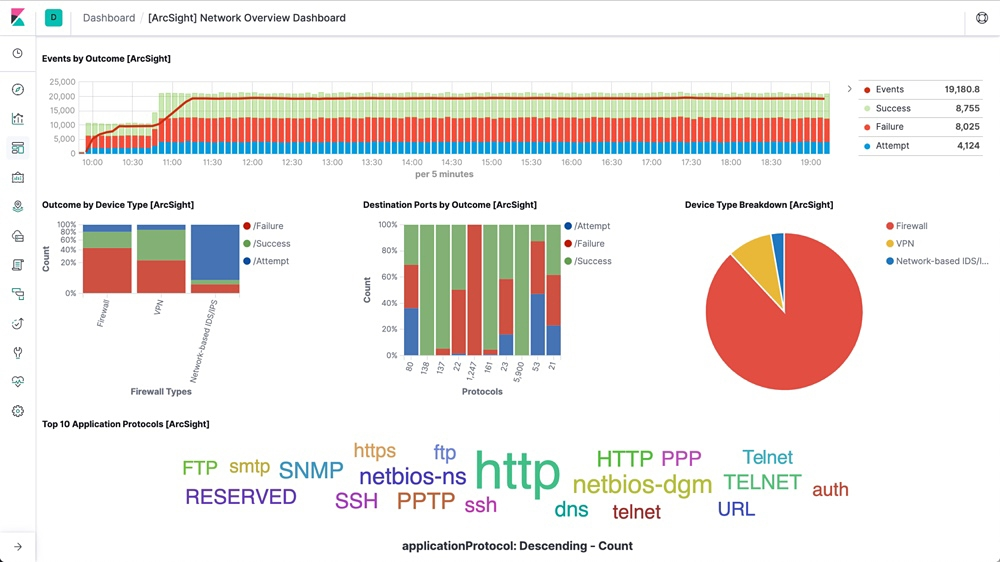 As logs from different on-premises and cloud-based sources can vary in their format, Logstash is used to ingest and transform these logs into a common format for further processing. It can automatically filter and parse your event messages for easier analysis and visualization. Logstash is commonly deployed along with Elasticsearch and Kibana as part of the ELK-stack, which is used by many large organizations for log management and analytics. Being open-source, the ELK stack provides a high level of flexibility.
As logs from different on-premises and cloud-based sources can vary in their format, Logstash is used to ingest and transform these logs into a common format for further processing. It can automatically filter and parse your event messages for easier analysis and visualization. Logstash is commonly deployed along with Elasticsearch and Kibana as part of the ELK-stack, which is used by many large organizations for log management and analytics. Being open-source, the ELK stack provides a high level of flexibility.
Fluentd
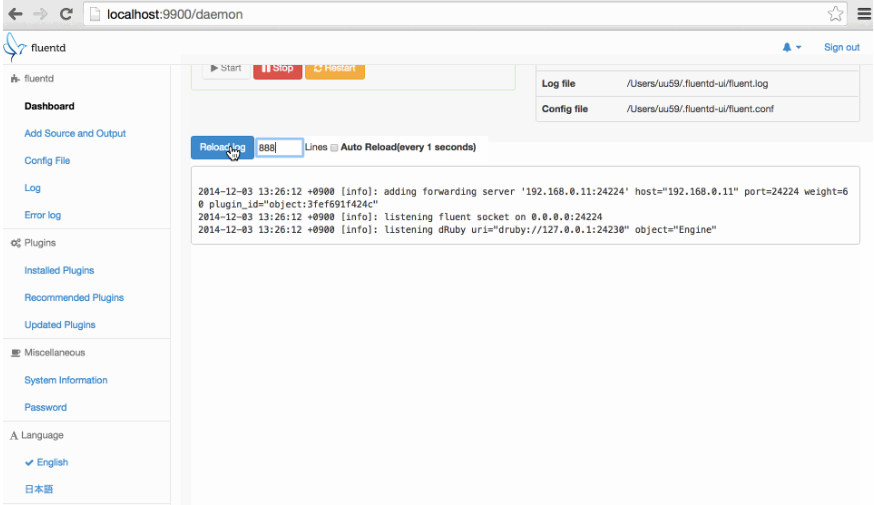 Organizations can also explore Fluentd in place of Logstash to create their log management and log analysis needs. Fluentd is also a log aggregator, which requires lower resource consumption than Logstash but may involve more complex configuration. A major advantage of using Fluentd is it structures your data as JSON, which is a commonly accepted structured data format. As logs are formatted in a common format, their parsing, filtering, buffering, querying, and analysis becomes more efficient.
Organizations can also explore Fluentd in place of Logstash to create their log management and log analysis needs. Fluentd is also a log aggregator, which requires lower resource consumption than Logstash but may involve more complex configuration. A major advantage of using Fluentd is it structures your data as JSON, which is a commonly accepted structured data format. As logs are formatted in a common format, their parsing, filtering, buffering, querying, and analysis becomes more efficient.
Rsyslog
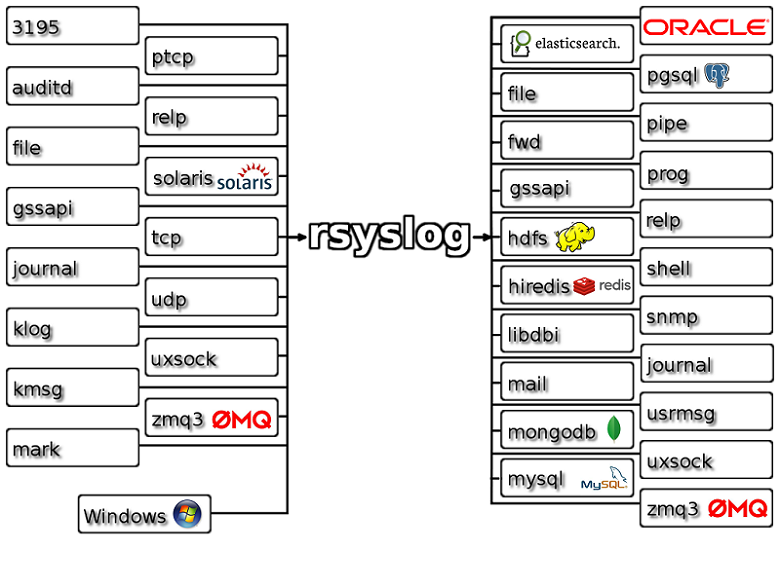 Rsyslog, another open-source log aggregator, claims to be the Swiss Army Knife of logging with features designed to support faster processing of logs. As shown in the image, it accepts all kinds of logs from different sources, transforms them into a common format, and forwards them to a preferred destination. With Rsyslog, organizations can transfer a large volume of log messages every second to local destinations without any heavy processing needs. However, when transferring messages to a remote destination, you may experience a performance lag.
Rsyslog, another open-source log aggregator, claims to be the Swiss Army Knife of logging with features designed to support faster processing of logs. As shown in the image, it accepts all kinds of logs from different sources, transforms them into a common format, and forwards them to a preferred destination. With Rsyslog, organizations can transfer a large volume of log messages every second to local destinations without any heavy processing needs. However, when transferring messages to a remote destination, you may experience a performance lag.
Syslog-ng 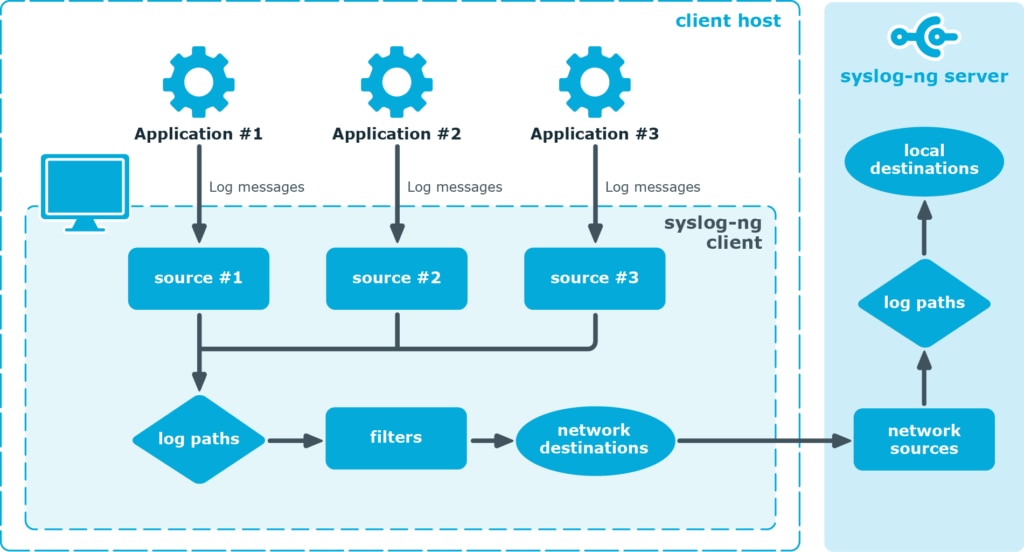
Syslog-ng is another well-known log aggregator, which can help you collect and route logs from any source to your desired destinations parallelly in near real time. This allows large organizations to transmit their logs to different locations, log viewers, and log analysis tools. Like other tools mentioned above, Syslog-ng can also automatically parse and format data and allows secure transfer over a wide range of protocols.
Papertrail
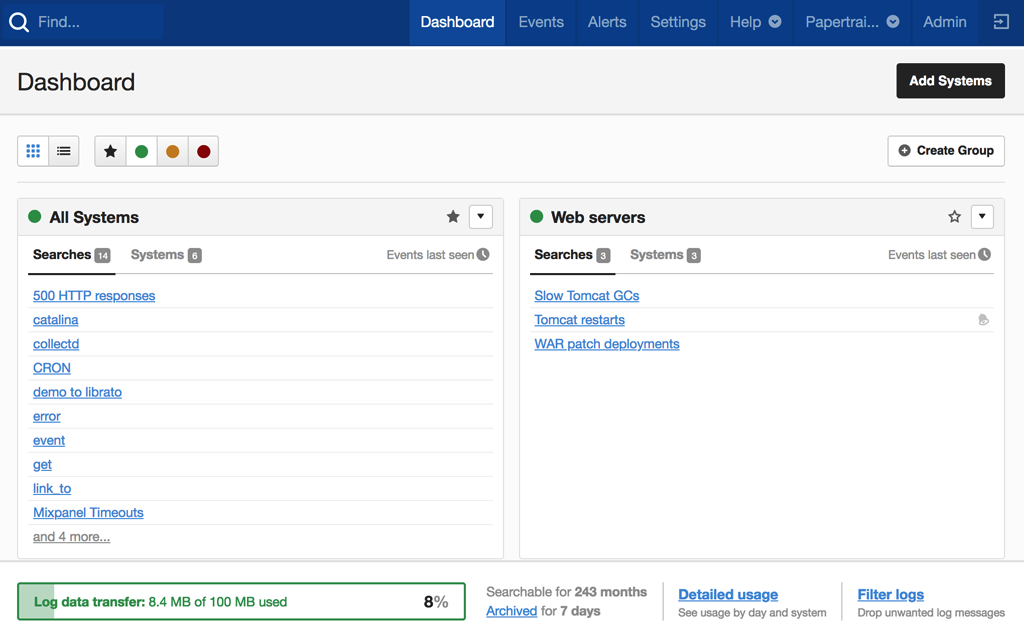
SolarWinds® Papertrail™ is a commercial Logging as a Service (LaaS) offering, which helps organizations manage and analyze their logs effortlessly. You can aggregate all your logs with Papertrail and use its event viewer for real-time analysis. The tool supports the live tail feature and presents log messages in the intuitive viewer, which provides a stream of log messages in an infinite scroll. It also allows you to query your logs using common search operators and provides quick results for search queries, even when searching through a massive volume of logs. Being a cloud-logging solution, Papertrail offers quicker setup without any elaborate configuration needs. You can also configure threshold-based alerts and integrate Papertrail with popular notification services like Slack, Hipchat, etc. to stay on top of your environment. Moreover, you can start using Papertrail now with a lifetime free trial.
Maximize log insights
Logs can tell you a lot about your IT systems’ health, performance, and security. They can capture details about system events and user activities and provide insights into errors and threats, improving troubleshooting and performance optimization efforts. However, you need to aggregate and centralize your logs to leverage all the data fully.
By implementing effective log aggregation techniques and using the right tools, your organization can gain better visibility, streamline operations, and enhance overall IT security and performance.
Ready to get the most out of your logs and increase your observability? Discover what Kiwi Syslog Server NG and Papertrail™ have to offer.
- Search, filter, and group logs: Aggregating logs allows you to quickly sift through log data to find the necessary information. Not only does log aggregation enable you to apply search queries, but it also means you can filter and group your logs. As a result, you can quickly locate relevant logs and diagnose issues.
- Troubleshoot faster: With the help of centralized logs, you can quickly detect anomalies, investigate root causes, and resolve incidents across your entire IT environment. Log aggregation helps reduce downtime and can lead to better overall system reliability.
- Collaborate efficiently: Log aggregation also facilitates better collaboration across your organization, as it can break down organizational silos and boost visibility. Teams can access the same up-to-date data from a centralized location, making collaboration faster and easier.
- Monitor in real time: Log aggregation also helps with real-time monitoring. Your team members can get real-time alerts for strange things, unexpected increases in activity, or possible security threats. This lets them take action right away before problems get worse.
- Improve security and compliance: By centralizing logs, your organization can proactively detect unauthorized access attempts, security breaches, policy violations, and suspicious activities. Additionally, maintaining a structured audit trail simplifies compliance with industry regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2, ensuring that all the necessary data is retained and easily accessible during audits.
Common log aggregation methods
There are several ways to aggregate logs. Standard methods include:
File replication
This log collection method involves copying log files originating from several sources to a centralized location for analyzing and sorting. You can use commands such as rsync or cron to copy log files, making the log aggregation process easy and fast. However, this log aggregation technique doesn’t allow for real-time monitoring and isn’t suitable for large organizations with high log volume.
Syslog
The system logging protocol (syslog) is a popular method for sharing log messages across an environment. Syslog messages are transferred with User Datagram Protocol (UDP) over port 514 and contain a header, structure data, and a message.
You can configure a syslog server to receive and store logs across your IT environment. Syslog data can be queried and is compatible with log aggregators. However, using syslog for log aggregation isn’t the most scalable solution.
Log forwarding
Sometimes, you may not need to take additional steps to collect logs as specific applications and servers have built-in log-forwarding capabilities. They can automatically transmit logs to your centralized logging system, allowing you to detect anomalies quickly and analyze data.
Application programming interfaces
It’s also worth noting that many cloud services and third-party applications provide application programming interfaces (APIs) that allow logs to be pulled programmatically. This scalable option can help you aggregate logs from your cloud platforms and software-as-a-service (SaaS) applications.
Streaming
Streaming log aggregation is an excellent option if your organization needs to handle a large amount of log data. Using protocols such as Netflow, SNMP, and IPFIX, this technique allows you to continuously collect, process, and forward logs in real time. Unlike batch-based methods, streaming log aggregation helps ensure that log data is available instantly for analysis. As a result, it can help you monitor security threats, detect performance issues, and respond to incidents as they occur.
Agent-based collection
You can also collect logs by deploying lightweight agents on your applications, servers, and devices. These agents will run in the background and continuously collect log data before forwarding it to your centralized logging system.
Agent-based log collection is incredibly efficient because it can preprocess logs before transmitting them. This includes structuring, filtering, and even compressing the logs, which can help reduce bandwidth consumption and storage costs.
Automated pipelines
Automated pipelines can streamline the entire process by automatically collecting, processing, and routing logs from multiple sources to a centralized storage and analysis system. Automated pipelines improve efficiency, reduce human error, and help ensure that your logs are consistently structured and processed by eliminating the need for manual intervention.
You can configure your pipeline to filter out unnecessary logs, enrich logs, standardize logs, mask sensitive data, trigger alerts, and more, saving you valuable time and energy. In addition to being highly customizable, automated pipelines are very scalable. They can handle large amounts of log data without impacting your system’s performance.
Steps in the log aggregation process
There are a few key steps to log aggregation that you should know about, including:
- Log collection: The first step in the process is to gather logs from multiple sources. These generally include servers, applications, devices, databases, and cloud services. This can be completed using APIs, agents, and syslog messages.
- Log parsing and normalization: After the logs have been collected, they must be processed and put into a standardized structured format. Parsing involves extracting key information from logs, including timestamps, error codes, and severity levels, simplifying log analysis. Normalizing the logs will allow you to efficiently correlate logs from different data sources.
- Centralized log storage: Aggregated logs should be stored in a centralized location. Usually, this means using on-premises log management or a cloud-based system. This makes logs more easily accessible, which can help when searching logs, demonstrating compliance, or preventing data loss.
- Log indexing: Next, all logs are indexed. This can increase data organization and allow for faster searching and filtering capabilities.
- Log enriching: Some log aggregation tools will add another step and enrich logs with more contextual information. For example, they may add the user ID, geolocation, or log correlation information.
- Log visualization: Log aggregation software also visualizes collected logs in easily understandable formats such as graphs, charts, or heat maps, which you can view using dashboards. With visualization, it’s much easier to spot spikes in errors, performance issues, and unusual activities.
- Alerting: Most log aggregation tools also have an alert functionality, meaning they can instantly notify your team of potential security threats, anomalies, system failures, etc.
- Automation: Some log aggregation solutions even have automated response capabilities. When a predefined condition or anomaly is detected, the tool can automatically act on your behalf. For example, it may restart certain services, block suspicious IP addresses, or send emails to predefined administrators.
Best Practices for Log Aggregation
Select a Reliable Protocol
There are three major protocols for transmitting log data:
- UDP (User Datagram Protocol) – A fast and resource-efficient protocol; however, lacks reliability as it doesn’t require acknowledgment of receipt (ACK). It also doesn’t support secure encryption of logs.
- TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) – Most commonly used protocol for streaming; adds reliability to every message transfer with ACK. However, requirements for the handshake and active connection makes it resource intensive.
- RELP (Reliable Event Logging Protocol) – The most reliable protocol, explicitly designed for Rsyslog. Like TCP it also involves the acknowledgment step and resends the log message if encounters an error. The protocol is commonly employed for log streaming in highly regulated industries unable to afford message loss.
Secure Log Transfers With Encryption
Logs may contain crucial information about customers’ personally identifiable information, financial data, and other business-sensitive data. Threat actors can use sophisticated sniffers to read your log data, and it becomes increasingly exposed when transmitted in clear text over the internet. Ensuring customer data is anonymized is an important step in information security. However, to add another layer of security, all log data should be encrypted using protocols such as TLS.
Use a Centralized Log Management Tool
You can create your own log management setup using open-source tools. However, when using open-source tools, you have to be ready for various configuration challenges. A self-managed logging setup requires multiple complex integrations, constant infrastructure monitoring, and significant time investment in maintenance and upgrades. On the other hand, commercial log management solutions offer quicker provisioning, higher scalability, greater performance, easier integration, dedicated technical support, and all this at a much lower Total Cost of Ownership (Total Cost of Ownership).
Best Tools for Log Aggregation and Management
Log aggregation tools are vital for organizations, as they can simplify the collection, storage, and analysis of log data from several sources. Without centralized logs, detecting security threats, troubleshooting issues, and maintaining compliance with various regulations can quickly become time-consuming and inefficient. On the other hand, the correct log aggregation tool can help you and your team quickly discover anomalies, accurately correlate events across different systems within your IT infrastructure, and automate alerts, enabling you to manage incidents proactively. There are plenty of log aggregation tools on the market, but two popular options are SolarWinds® Kiwi Syslog® Server NG and Papertrail™.
Kiwi Syslog Server NG

Kiwi Syslog Server NG is a new and improved version of Kiwi Syslog Server. This powerful solution can manage syslog messages, SNMP traps, and Windows event logs, yet it remains affordable and simple to use. Since it can centralize all your syslog messages, Kiwi Syslog Server NG can save you valuable time in discovering the root cause of an issue or resolving network problems.
Kiwi Syslog Server NG has powerful filtering capabilities, meaning you can view messages based on severity, time, hostname, and more. It can also automatically alert you of specific events or even act independently. For example, it can send email notifications; generate reports; run scripts; run external programs; write logs to a file, Windows event log, or database; forward syslog messages and SNMP traps to another host; or split written logs by IP, device, date, or hostname.
Logstash
 As logs from different on-premises and cloud-based sources can vary in their format, Logstash is used to ingest and transform these logs into a common format for further processing. It can automatically filter and parse your event messages for easier analysis and visualization. Logstash is commonly deployed along with Elasticsearch and Kibana as part of the ELK-stack, which is used by many large organizations for log management and analytics. Being open-source, the ELK stack provides a high level of flexibility.
As logs from different on-premises and cloud-based sources can vary in their format, Logstash is used to ingest and transform these logs into a common format for further processing. It can automatically filter and parse your event messages for easier analysis and visualization. Logstash is commonly deployed along with Elasticsearch and Kibana as part of the ELK-stack, which is used by many large organizations for log management and analytics. Being open-source, the ELK stack provides a high level of flexibility.
Fluentd
 Organizations can also explore Fluentd in place of Logstash to create their log management and log analysis needs. Fluentd is also a log aggregator, which requires lower resource consumption than Logstash but may involve more complex configuration. A major advantage of using Fluentd is it structures your data as JSON, which is a commonly accepted structured data format. As logs are formatted in a common format, their parsing, filtering, buffering, querying, and analysis becomes more efficient.
Organizations can also explore Fluentd in place of Logstash to create their log management and log analysis needs. Fluentd is also a log aggregator, which requires lower resource consumption than Logstash but may involve more complex configuration. A major advantage of using Fluentd is it structures your data as JSON, which is a commonly accepted structured data format. As logs are formatted in a common format, their parsing, filtering, buffering, querying, and analysis becomes more efficient.
Rsyslog
 Rsyslog, another open-source log aggregator, claims to be the Swiss Army Knife of logging with features designed to support faster processing of logs. As shown in the image, it accepts all kinds of logs from different sources, transforms them into a common format, and forwards them to a preferred destination. With Rsyslog, organizations can transfer a large volume of log messages every second to local destinations without any heavy processing needs. However, when transferring messages to a remote destination, you may experience a performance lag.
Rsyslog, another open-source log aggregator, claims to be the Swiss Army Knife of logging with features designed to support faster processing of logs. As shown in the image, it accepts all kinds of logs from different sources, transforms them into a common format, and forwards them to a preferred destination. With Rsyslog, organizations can transfer a large volume of log messages every second to local destinations without any heavy processing needs. However, when transferring messages to a remote destination, you may experience a performance lag.
Syslog-ng 
Syslog-ng is another well-known log aggregator, which can help you collect and route logs from any source to your desired destinations parallelly in near real time. This allows large organizations to transmit their logs to different locations, log viewers, and log analysis tools. Like other tools mentioned above, Syslog-ng can also automatically parse and format data and allows secure transfer over a wide range of protocols.
Papertrail

SolarWinds® Papertrail™ is a commercial Logging as a Service (LaaS) offering, which helps organizations manage and analyze their logs effortlessly. You can aggregate all your logs with Papertrail and use its event viewer for real-time analysis. The tool supports the live tail feature and presents log messages in the intuitive viewer, which provides a stream of log messages in an infinite scroll. It also allows you to query your logs using common search operators and provides quick results for search queries, even when searching through a massive volume of logs. Being a cloud-logging solution, Papertrail offers quicker setup without any elaborate configuration needs. You can also configure threshold-based alerts and integrate Papertrail with popular notification services like Slack, Hipchat, etc. to stay on top of your environment. Moreover, you can start using Papertrail now with a lifetime free trial.
Maximize log insights
Logs can tell you a lot about your IT systems’ health, performance, and security. They can capture details about system events and user activities and provide insights into errors and threats, improving troubleshooting and performance optimization efforts. However, you need to aggregate and centralize your logs to leverage all the data fully.
By implementing effective log aggregation techniques and using the right tools, your organization can gain better visibility, streamline operations, and enhance overall IT security and performance.
Ready to get the most out of your logs and increase your observability? Discover what Kiwi Syslog Server NG and Papertrail™ have to offer.

