We all know measuring network performance is important. When a network experiences downtime or an end user reports a performance issue, network administrators and engineers will rely heavily on network performance measurements to rectify the problem. They might use IP service-level agreements, or IP SLAs, to do this.
But exactly what is IP SLA technology, and how is it used? I’ve created this guide to answer these questions. I’ll also look at one of the best IP SLA management tools on the market, SolarWinds® VoIP & Network Quality Manager (VNQM), which uses IP SLA technology to deliver a comprehensive, detailed, and advanced monitoring and management solution.
Table of contents:
What Is IP SLA?
Benefits of IP SLA
How to Use IP SLA to Monitor Network Performance
The Best IP SLA Management and Monitoring Tool
What Is IP SLA?
IP SLA stands for “IP service-level agreement.” It’s a Cisco development designed to provide a means of conducting network diagnostics. IP SLAs generate traffic between Cisco IOS devices connected to your network, then analyze the traffic. The generated traffic is a simulation of network data and IP services, which allows network performance metrics to be collected in real time.
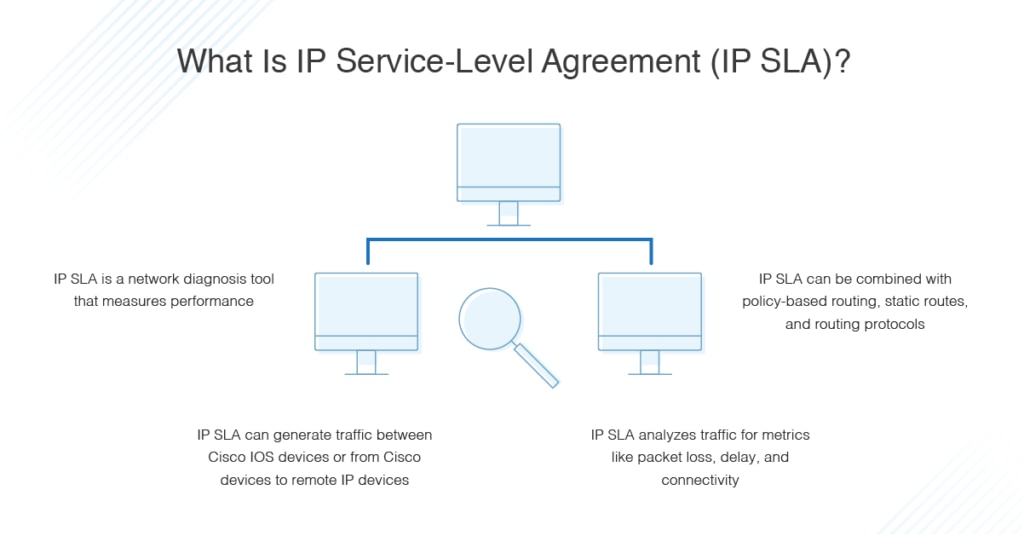
IP SLAs can also be used to analyze traffic between Cisco IOS devices and remote IP devices, like an application server. The measurements collected from traffic analysis can be useful for conducting problem analysis, troubleshooting, and creating topologies of your networks.
Put simply, an IP SLA measures network performance. IP SLAs can take different forms, from a ping measuring round-trip time to a voice-over IP RTP packet checking jitter, delay, and mean opinion score (MOS), giving you insight into voice quality.
There are a lot of ways to measure network performance. IP SLAs stand out because they can be combined with policy-based routing, static routes, and routing protocols (e.g., EIGRP and OSPF).
For certain Cisco IOS IP SLA processes, monitored network performance statistics are stored in both SNMP MIBs and the command-line interface (CLI). IP SLA packets will have options configurable at the application and IP layer. These include source IP address, destination IP address, type of service, URL web address, VPN, routing or forwarding instance, and UDP or TCP port numbers.
One of the benefits of using IP SLAs is they’re independent of layer 2 transport. This means you can establish end-to-end operations across disparate networks to reflect the metrics most likely to impact the end user’s actual experience. IP SLAs can collect a subset of the following metrics:
- Path
- Packet loss
- Jitter
- Delay
- Connectivity
- Packet sequencing
- Website or server download time
Benefits of IP SLA
As noted above, there are obvious benefits to using IP SLAs for network performance monitoring, including the ability to measure latency, packet loss, and jitter. Moreover, IP SLAs are known for affording users continuous and reliable measurements. But there’s more to IP SLAs than network monitoring benefits. Here are some other advantages associated with the use of IP SLAs:
- IP service network health assessments, for confirming an existing QoS is suitable for new IP services
- Network verification and performance monitoring of multi-protocol label switching (MPLS) and virtual private networks
- Service-level agreement measurement, monitoring, and verification
- Network availability monitoring on an edge-to-edge basis to facilitate network resource connectivity and verification testing
- Rapid network operation troubleshooting through dependable and consistent measurements
- VoIP performance monitoring
How to Use IP SLA to Monitor Network Performance
An IP SLA uses generated traffic to measure the network performance between two networking devices. The IP SLA begins when a device (the source) sends a generated packet to another device (the destination). Once this packet is received, the destination device responds with time-stamp information, depending on the type of IP SLA operation used. This information is then used by the source device to make a performance metric calculation. A specific protocol, like UDP, is used to conduct this IP SLA operation.
To conduct an IP SLA measurement, follow these instructions:
- If required, enable the IP SLA responder.
- Configure the operation type you require.
- If there are options for the operation type available, configure them.
- If necessary, configure any threshold conditions.
- Schedule the operation, then allow it to run for a set time.
- View the results and interpret them using either the Cisco IOS CLI or an SNMP-enabled network management system.
This is a complicated process and is likely to raise a few questions for beginners. You might be asking: what is an IP SLA responder? What are threshold conditions, and why are they important? How do I schedule operations? I’ve answered these questions below.
What Is an IP SLA Responder?
The responder is a component location in the destination device, which allows it to anticipate and reply to request packets. It uses the Cisco IOS IP SLAs Control Protocol and allows accurate measurements to be taken without any need for probes. For a destination IP SLA responder, only a Cisco IOS device can be the source. Certain operations, like Telnet or HTTP, do not require a responder.
What Are Threshold Conditions?
Threshold monitoring is an important element of using IP SLAs. You must have systems in place to keep you informed of any breaches. IP SLAs can send SNMP traps, which can be triggered by different conditions, including timeout, loss of connection, the average jitter threshold, one-way packet loss, the round-trip time threshold, one-way jitter, one-way latency, and one-way MOS.
You are also able to use IP SLA thresholds to trigger other IP SLA operations, so further analysis can be conducted. For instance, you could increase the frequency or initiate an ICMP path jitter operation.
How Do I Schedule Operations?
Once your IP SLA operation has been configured, it’s time to schedule the operation so it can start gathering statistics. An operation can be scheduled to start instantly, at a certain time, or on a specific date. If you choose the “pending” option, you can schedule an operation, so it begins later. The pending state can also be used when an operation is reactionary (e.g., if it’s a threshold operation triggered if there’s a specific breach). IP SLA operations can be scheduled individually or in bulk.
If you choose to schedule multiple IP SLA operations, you can use a single command via the Cisco RTTMON-MIB or the Cisco IOS CLI. You can also schedule the operations, so they run at evenly distributed times, which lets you manage the amount of monitoring traffic, minimizing CPU utilization and improving the scalability of the network.
Best IP SLA Management and Monitoring Tool
Using IP SLAs to monitor your network isn’t easy, and there’s a significant learning curve when you’re starting out. To save yourself time, not to mention the resources and labor associated with embarking on IP SLA management, you may want to employ an IP SLA monitoring solution.
IP SLAs are SNMP accessible, which means they can be used by performance monitoring programs. An effective network monitor and manager can streamline IP SLA management, minimize errors and inaccuracy, and make IP SLA network performance measurements more actionable and accessible.
SolarWinds VoIP & Network Quality Manager combines a range of performance monitoring functionalities with user-friendliness. This solution is designed to grow with you, offering enterprise-grade capacity without compromising on ease of use. The user interface is dynamic, with a logical and intuitive layout, and measurements are graphically represented in the form of graphs and charts where appropriate.
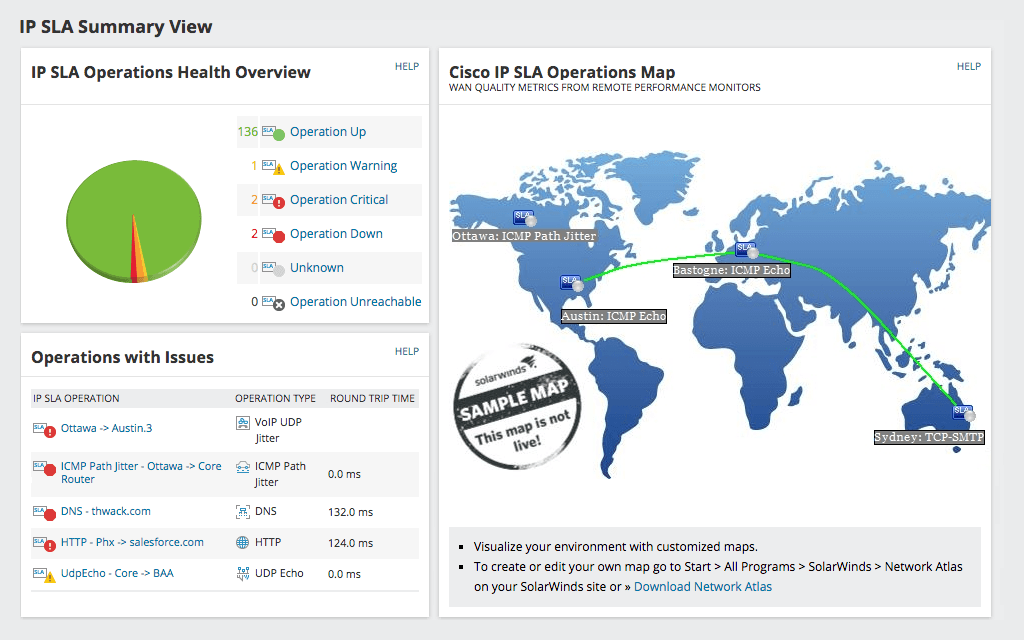
VNQM is extremely feature-rich (complete list here), allowing you to monitor VoIP call QoS metrics like latency, packet loss, jitter, and MOS; correlate call problems with WAN performance to facilitate troubleshooting at an advanced level; search and filter all records of call details; and monitor site-to-site WAN performance. It can even discover all Cisco IP SLA-enabled devices on your network automatically, with full deployment of the program taking less than an hour.
With VNQM, you don’t have to perform complex CLI commands to add IP SLA operations. Instead, you can rely on the step-by-step wizard, which walks you through the process of adding operations in a straightforward way. For increased flexibility, you have the option of choosing between four IP SLA deployment methods: simple, fully meshed, hub-and-spoke, or custom.
IP SLA operation thresholds can be customized to suit the needs of you and your network. You can monitor numerous IP SLA operations at the same time, helping you determine which applications are most affected by poor WAN performance. VNQM supports a broad range of IP SLA operations, including FTP for measuring the round-trip time to transfer a file, HTTP for measuring the round-trip time to access a web page, DNS for measuring the DNS lookup time, TCP for measuring the connection time, and much more.
Overall, SolarWinds VNQM is a versatile and advanced IP SLA management and monitoring solution. It streamlines your monitoring operations and keeps you informed with alerts that can be configured to notify you when specific thresholds are breached. It can be tailored to your requirements, with custom deployment and thresholds, and can accommodate massive growth. This tool takes all the hassle out of using IP SLAs to perform network monitoring, and it comes highly recommended. A 30-day free trial is available.
