It’s common nowadays for employees to use their own devices for work-related activities. While this can be beneficial and improve employees’ experiences, it also has some drawbacks. In this post, we will look at what bring your own device (BYOD) is and how organizations can implement policies and tools to help mitigate BYOD issues. Without further ado, let’s get started.
Why Is BYOD Security Important?
Preparing a BYOD Policy (What to Have in Mind)
BYOD and IP Infrastructure Challenges
5 Best Software for BYOD Management
1. SolarWinds IP Address Manager (Free Trial)
2. SolarWinds User Device Tracker (Free Trial)
3. ManageEngine Mobile Device Manager Plus
What Is BYOD?
BYOD is the practice of allowing employees to use their own devices for work or business-related activities, such as connecting to a shared network and accessing data either on-site (employees use the devices at work) or remotely (employees work at home). Smartphones, desktop computers, laptops, external storage (like flash drives), tablets, and other similar gadgets are examples of personal devices.
Pros & Cons of BYOD
The BYOD Policy can enhance productivity in a workplace but also involves some threats. Before making any decisions is essential to know about the disadvantages and advantages of implementing BYOD.
Pros of BYOD
BYOD can provide several benefits, including:
- Increased flexibility for employees
- Reduced IT costs for the company
- Improved efficiency and productivity
With BYOD, employees can use their preferred devices, improving their satisfaction and productivity.
Additionally, the company can save on hardware and labor costs by allowing employees to use their own devices. Finally, BYOD can reduce the need for training and support, saving time and improving the organization’s overall efficacy and productivity.
Cons of BYOD
BYOD policies can pose a potential security risk to company data. Employees’ personal devices may have weaker security measures and configurations, making it easier for hackers to access the company’s data.
Additionally, the company’s data may be at risk if an employee’s device is lost or stolen. Furthermore, inadequate firewall and antivirus protection on employee devices can lead to intrusions into the company’s network, and malware on an employee’s device can corrupt data.
What Is the Risk of BYOD?
While BYOD has many benefits, there are some risks associated with it that shouldn’t be overlooked. As stated above, one main issue with BYOD is that the company’s data is at risk, as a breach of some kind at some point is all but inevitable. For example, an employee’s device can potentially expose organizational data and credentials.
This can occur in a variety of ways, including the following:
- Employee devices may be lost or stolen. Attackers can acquire access to the company’s credentials, data, and network by gaining access to employee devices.
- Some employees may be reluctant to update their devices to the most recent security fixes. Suppose an employee’s device is not kept secure by updating it or installing antivirus software on a regular basis. In that case, an attacker can use the flaws to obtain access to the employee’s devices.
- Employees may get malware onto their devices designed to spread inside the company.
Attackers have created several websites and programs on the internet to spy on employee data and credentials. Employees may install those apps on their devices or browse websites while unaware they’re being spied on.
Why Is BYOD Security Important?
As reported by Bitglass, 82% of organizations enable the use of BYOD in their workplace. Due to the increasing adoption of BYOD, organizations must put in place security measures to mitigate any threats that could emerge from BYOD.
BYOD security is essential because it ensures a win-win situation for both employees and organizations. Employees can use the device they choose without jeopardizing the company. BYOD security helps enforce procedures that reduce risks like data loss, breaches, etc.
Preparing a BYOD Policy (What to Have in Mind)
BYOD policies outline the rules and criteria that employees and organizations must follow to use BYOD. However, before you can implement a BYOD policy, there are several things you need to consider.
Data Regulatory Considerations
Because BYOD refers to employee devices, you must ensure that the custom BYOD policy you create complies with existing data regulatory policies such as GDPR, HIPAA, and so on, so that your policy supports and conforms to protection and privacy for employee data.
Security Considerations
You must consider the type of security measure you’ll use to protect corporate data from any type of threat.
There are various security measures you can use, but at the very least, the BYOD policy should be able to do one of the following:
- Encrypt corporate data in transit and at rest.
- Use containerization to help segregate corporate data from employee personal data.
- Block unwanted websites or connections to Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, etc.
Employee Considerations
It’s critical to keep in mind employee welfare while developing a BYOD policy. Some important factors to consider are:
Privacy: Employees may be concerned that their organization is prying into their personal lives. As a result, a BYOD policy should clearly identify ways to ensure that employee personal data is protected and not accessible without proper authorization.
Convenience: A BYOD policy should provide flexibility while being convenient for employees. Employees’ abilities to use their own devices shouldn’t be restricted by policy.
Training: Employees should be trained to utilize their devices for work-related purposes. This training will guarantee that employees can use their devices successfully and in accordance with company rules.
Also, consider managing application and business data on employee devices so that all data may be readily wiped when the employee departs the organization. You can do this using technologies enabling your company to install, update, and delete software on employee devices. You should also run security audits to ensure that employees adhere to the standards and follow the BYOD policy regulations.
BYOD and IP Infrastructure Challenges
As the number of employee devices in an organization grows, the company’s IP infrastructure becomes more complex. For example, when the number of BYOD devices increases, it’ll be more difficult to track the tasks performed by each device. This is where BYOD solutions can help, as they provide a way for companies to manage and secure the use of personal devices on their network. These solutions enable employees to use their personal devices for work while providing the protection and control enterprises require to secure their networks and data.
As the number of employee devices in an organization grows, the company’s IP infrastructure becomes more complex.
For example, when the number of BYOD devices increases, it’ll be more difficult to track the tasks performed by each device. This is easier with enterprise devices since the number of such devices is inherently limited, while each employee can use any number of their own devices.
Another difficulty with BYOD is that organizations must scale up their IT infrastructure to assure IP address provisioning and management to prevent issues such as insufficient space allocation, IP address conflict, etc. One solution is to have a platform that provides real monitoring and management capability, allowing for unified IP infrastructure transparency.
5 Best Software for BYOD Management
1. SolarWinds IP Address Manager (Free Trial)
SolarWinds® IP Address Manager (IPAM) is a network management solution that assists businesses in managing their IP addresses and network infrastructure. It provides a centralized platform for monitoring and analyzing network consumption and performance and monitoring and managing IP address space allocation.
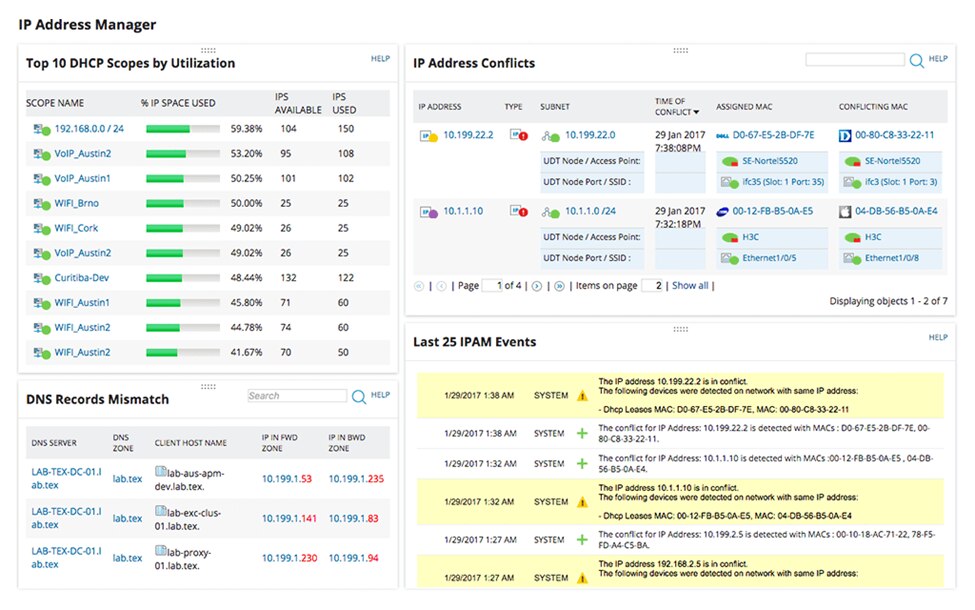
Because of the growing number of BYOD devices in an organization, it’s critical to manage the IP addresses and network infrastructure efficiently, and this can be done by having software that provides a transparent view of the entire infrastructure. IPAM does so through intuitive dashboarding and reports that keep track of IP addresses and events and provide a view into IP address space allocation. This allows you to identify occurring issues so proper measures can be taken.
SolarWinds IP Address Manager also monitors DNS and DHCP servers. You can download a free trial – it provides complete visibility into your IP infrastructure, and it has intuitive dashboards and reports for IP tracking.
Download Free Trial Learn More
2. SolarWinds User Device Tracker (Free Trial)
SolarWinds® User Device Tracker (UDT) is a network management solution that allows companies to track and monitor the devices that are connected to their network using their IP address, username, or Mac address. It provides a single platform for monitoring and managing connected devices and tracking and analyzing network usage and performance. UDT offers numerous features such as device tracking, network monitoring, device classification, security, etc.
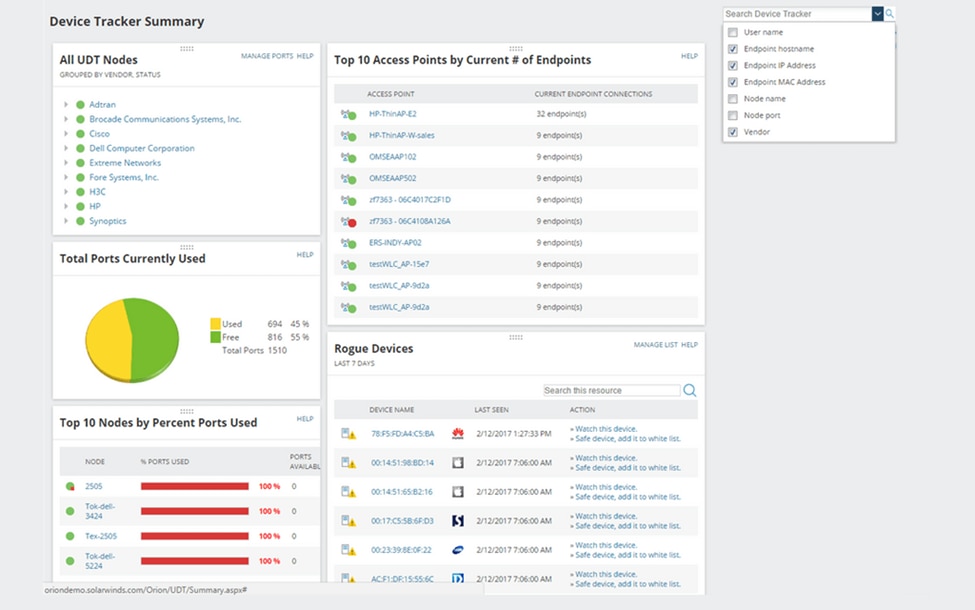
SolarWinds User Device Tracker provides easy tracking of all devices connected to the corporate network.
Download Free Trial Learn More
3. ManageEngine Mobile Device Manager Plus
ManageEngine Mobile Device Manager Plus is a full-suite BYOD platform that includes app management, device management, security management, and more. Some features include the containerization of corporate apps from personal apps that prevent sharing corporate data via USB devices, screenshots, clipboards, and so on. It supports several operating systems and can be installed on-premises or in the cloud.
ManageEngine Mobile Device Manager Plus offers a range of mobile device management features, including app containerization and remote data wiping. It supports all types of devices, including smartphones, laptops, TVs, and IoT devices.
Additionally, it provides robust device security.
4. Scalefusion
Scalefusion is a BYOD tool that offers application management, device management, and other features. It provides capabilities such as the containerization of business data from personal data and the seamless management of apps on staff devices, such as installation, upgrades, and uninstallation without user intervention. Scalefusion is compatible with multiple operating systems, including Windows, MacOS, iOS, and Android.
Scalefusion offers a range of mobile device management features, including app containerization, remote data wiping, and data sharing restrictions. However, it doesn’t support a wide variety of devices and operating systems, such as Linux and ChromeOS.
5. N-able N-sight RMM
N-able is a remote monitoring and management platform for BYOD devices that allows you to monitor, secure, and manage them. It has capabilities such as automation (the ability to drag and drop data on devices), patch management, network device monitoring, security, and more. It works on a variety of platforms, including Windows, MacOS, iOS, and Android, and it supports a wide range of devices, including mobile devices, PCs, Macs, IoT devices (such as Raspberry Pi), and so on.
The advantages of N-able include provisioning of mobile device management and ability to monitor the device on the go, etc. However, it doesn’t provide complaint reporting.
Conclusion
BYOD refers to the practice of allowing employees to use their own devices for work-related purposes. In this post, we discussed what BYOD is, some of the risks it poses, and possible BYOD solutions that can be used to mitigate those risks, such as adopting strong security policies, as well as employing software tools like SolarWinds IP Address Manager, UDT, and others.
This post was written by Ibrahim Ogunbiyi. Ibrahim is a data scientist and an IT support specialist. He loves writing anything about data and IT operations.

